
Often, especially for sensitivity analysis, simulations are conducted many times and only one or a few parameters are changed meaning the networks stays constant. Then, especially for resource consuming network builders it is a good idea to generate the network once and store it. MoRe provides suitable features:
Typically, the GRAPHML file is also produced by MoRe using MoreIoUtilities#outputGraph()
For details, see JavaDoc of MGeoRsRestoreNetworkBuilder. The test class MGeoRsRestoreNetworkBuilderTest contains a complete example.
The builder implements MoreGeoNetworkBuilder in order to substitute such network builders. However, it can also be used to restore networks for agents that are not geographically rooted.
Network generators that support addition and removal of edges extend MoreNetworkEdgeModifier. Implementations often depend on the target system like Repast Simphony (MGeoRsNetworkEdgeModifier). Example: MBaselineDhhRadiusNetworkBuilder extends MGeoRsNetworkService, which uses a MGeoRsNetworkEdgeModifier.
Often, the method addAndLinkNode needs to specified by the network generator by themselves since the way a node is linked a network is not general (e.g. MBaselineDhhRadiusNetworkBuilder). The MoreNetworkEdgeModifier can be used in these implementations.
NetworkService classes usually combine the MoreNetworkBuilder and the MoreNetworkModifier interfaces.
There is an interface MoreGeoNetworkEdgeModifier for edge modifiers that support geographies. However, the user needs to take care to assign such a MoreNetworkEdgeModifier to the network generator that shall support geographies.
The component approach in network generation and manipulation is much more flexible than encapsulating all network operations within the network object. It allows using e.g. different edge modifiers as ones that have geography support only in certain contexts, for instance initialisation or for certain model configurations.
The MGeoRsHomophilyDistanceFfNetworkService seeks to incorporate important features for ABM:
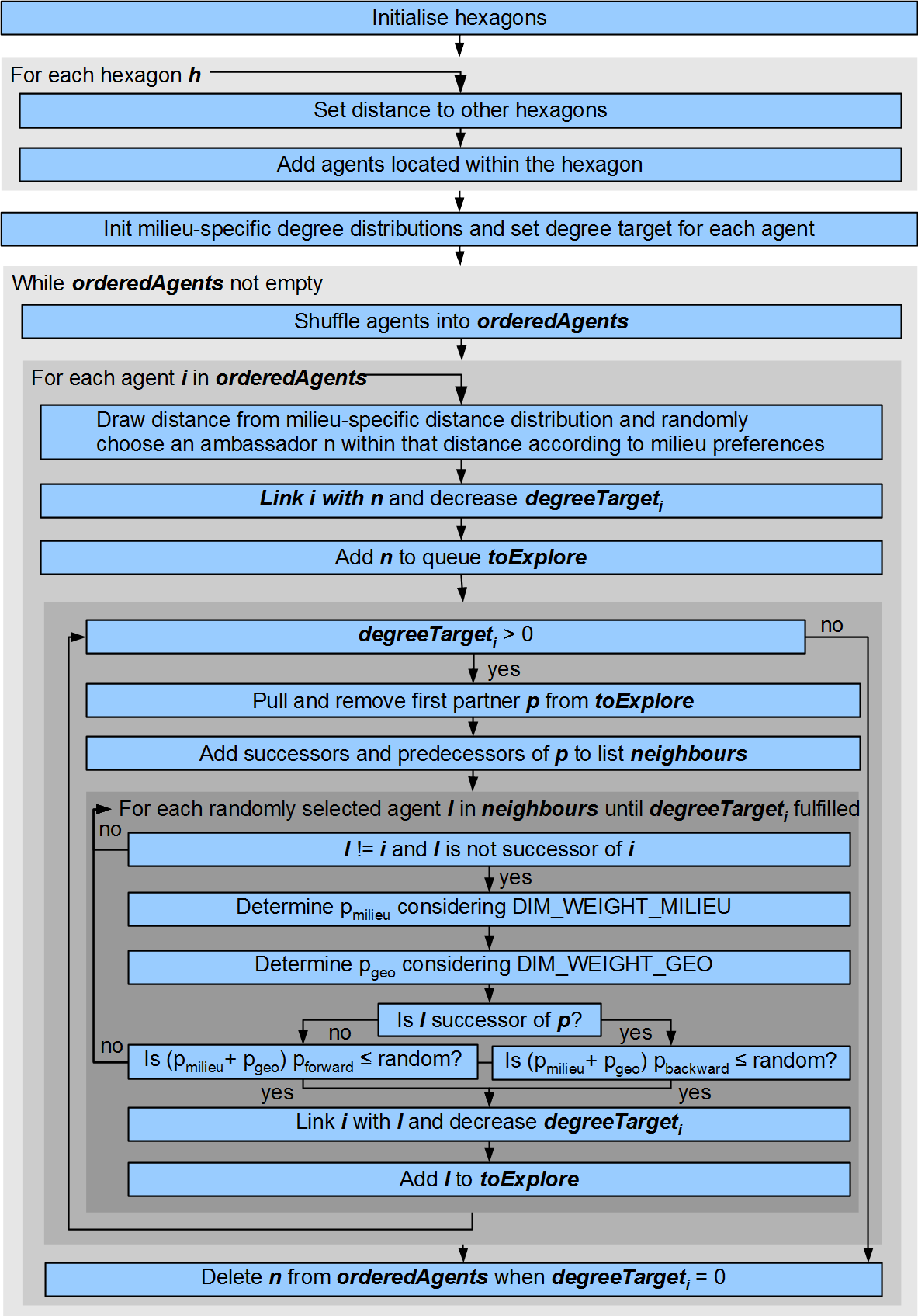
Apart from the milieu composition preferences, degree and distance distributions, the algorithm considers two important parameters that allow to control the resulting networks modularity quite well:
Two more parameters are important to adjust the precision for milieu composition and distance distribution (Note that the sum of both has to be 1.0):
See MGeoRsHomophilyDistanceFfNetworkService for a list of all relevant parameters.
Hexagon shapefiles are required to determine distances between agents. Since the size of hexagons depends on the simulation region and desired performance, often according hexagon shapefiles need to be created anew (and the filename assigned to parameter MNetBuildHdffPa#HEXAGON_SHAPEFILE.
NOTE: The hexagon shapefile must cover all agent positions and should not be much larger since it is used to calculated the area's diameter which is used to initialised the distance distributions!
There are two ways to produce appropriate hexagon shapefiles:
The python scripts are available at . There is one for squared model areas and one for arbitrary model regions using a raster file as input (or a shapefile to use subsequently in the process).
| Left X | -150 |
| Width | 1300 |
| Bottom Y | -150 |
| Height | 1200 |
| H Spacing | 200 |
| V Spacing | auto |
There are several ways to implement network generators that comply with the various MoRe interfaces:
To specify a general network generator as RS and/or geography network generator it is normally sufficient to
Network Builders should have at least two constructors: